
IoT communication protocols play a crucial role in determining the efficiency, range, and power consumption of connected devices. Among the most widely used protocols in IoT gateways are WiFi, LoRaWAN, and Zigbee. Each protocol offers unique advantages and is suited for specific applications in utility monitoring, smart grids, and industrial automation. This guide compares these three protocols to help you choose the best solution for your needs.
What Is the Difference Between LoRaWAN and Zigbee?
LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network)
Range: Long-range communication up to 15 km in rural areas and several kilometers in urban settings.
Power Consumption: Ultra-low power, making it ideal for battery-operated devices.
Data Rate: Lower data rates suitable for infrequent, small data transmissions.
Applications: Best for wide-area utility monitoring, such as water, gas, and electricity systems.
Zigbee
Range: Short to medium range, typically up to 100 meters indoors.
Power Consumption: Low power consumption, suitable for mesh networking.
Data Rate: Higher data rates compared to LoRaWAN, ideal for more frequent data transmissions.
Applications: Best for smart home devices and indoor utility monitoring where range is less critical.
Benefits of WiFi-Based IoT Communication for Utilities
WiFi
Range: Medium range, typically up to 100 meters indoors.
Power Consumption: Higher power consumption compared to LoRaWAN and Zigbee.
Data Rate: High data rates suitable for real-time, high-volume data transmissions.
Applications: Best for applications requiring high bandwidth, such as video surveillance or detailed real-time utility monitoring.
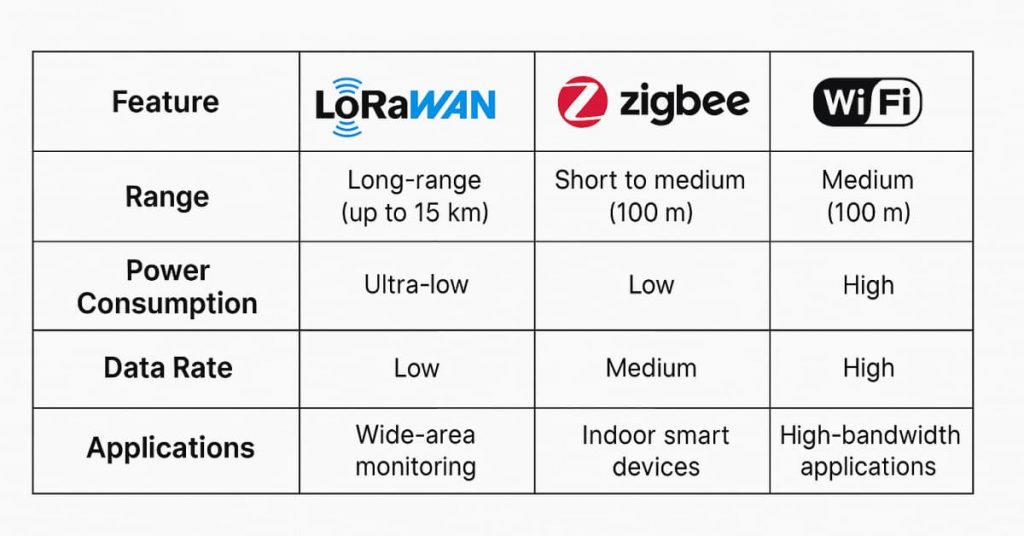
IoT Gateway Protocol Comparison
| Feature | LoRaWAN | Zigbee | WiFi |
| Range | Long-range (up to 15 km) | Short to medium (100 m) | Medium (100 m) |
| Power Consumption | Ultra-low | Low | High |
| Data Rate | Low | Medium | High |
| Applications | Wide-area monitoring | Indoor smart devices | High-bandwidth applications |
How to Choose Between LoRaWAN, Zigbee, and WiFi
Consider Range Requirements:
Choose LoRaWAN for wide-area coverage, such as utility grids or industrial facilities.
Opt for Zigbee in compact environments like homes or small offices.
Select WiFi for medium-range applications needing high data rates.
Evaluate Power Consumption:
Use LoRaWAN for battery-powered devices requiring long operational lifespans.
Select Zigbee for low-power mesh networks.
Opt for WiFi when power consumption is less critical.
Analyze Data Needs:
LoRaWAN is best for transmitting small amounts of data infrequently.
Zigbee balances data rates with power efficiency for frequent communication.
WiFi excels in high-data scenarios, such as streaming or real-time analytics.
IoT Gateway Protocol Applications
LoRaWAN
Utility monitoring (water, gas, electricity).
Smart agriculture and environmental monitoring.
Long-range industrial IoT systems.
Zigbee
Smart home automation (lighting, thermostats).
Indoor utility monitoring.
Short-range industrial applications.
WiFi
Video surveillance for smart utilities.
Real-time utility analytics.
High-bandwidth smart grid applications.
Buy IoT Gateways with Multiple Protocol Support
For reliable IoT gateways that support LoRaWAN, Zigbee, and WiFi, explore:
Final Thoughts
Choosing the right IoT gateway protocol depends on your specific application needs, including range, power consumption, and data requirements. LoRaWAN, Zigbee, and WiFi each offer unique advantages that cater to different use cases in utility management, industrial automation, and smart grids.
Invest in Jooby’s advanced IoT gateways to find the perfect solution for your smart utility systems.
